November saw the conclusion of Google’s Core Update rollout, its fourth update of the year. In this article, we’ve covered the impact of this latest update, as well as the winners and losers.
We’ve also covered how Google is working on improving structured data markup for companies in search results and introducing AI-driven generative summaries.
The search algorithm now values firsthand knowledge, introducing a ‘follow’ feature for users. There’s also an experimental ‘Notes’ feature allowing users to add personal tips to search results. However, the crawl rate limiter tool will be removed from Google Search Console in January 2024.
In a nutshell, Google’s updates emphasise AI-driven search experiences, user-focused content, and continuous adaptation in SEO strategies to align with these changes.
Allow our traffic light system to guide you to the articles that need your attention, so watch out for Red light updates as they’re major changes that will need you to take action, whereas amber updates may make you think and are worth knowing but aren’t urgent. And finally, green light updates which are great for your SEO and site knowledge but are less significant than others
Keen to know more about any of these changes and what they mean for your SEO? Get in touch or visit our SEO agency page to find out how we can help.
In this post, we’ll explore:
- Google November 2023 concludes its core update rollout?
- Google enhances search with support for organisation metadata
- Google SGE & generative summaries for search results patent
- What is Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE)?
- What is the US11769017B1 patent?
- What does this mean for SEO professionals and their strategies?
- Google rankings prioritise first-hand knowledge
- What does this mean for SEO?
- Google launches “Notes” to add user comments in search results
- Google removing crawl rate limiter tool from Search Console
- Google search algorithm ranking continues?
- Google’s 2023 search quality rater guidelines update: Here’s what changed?
- Enhanced guidance on rating forum and Q&A page quality, particularly for new discussions or those exhibiting "combative," "misleading," or "spammy" content
- Emphasis on user location's relevance to certain queries and its influence on search results
- Detailed explanations on "Minor Interpretations," categorising them into "reasonable," "unlikely," and "no chance" interpretations
- Further clarification of 'Know Simple' and 'Do' queries, outlining specific types of queries that don't fit the "Know Simple" criteria
- Expanded examples of "Know Simple Queries," "Know Queries," and "Do" queries, offering insights into queries best answered through videos, images, or how-to guides
- Examples of SERP features that highly satisfy user needs, with explanations on why these particular results are rated as "highly meeting" user expectations
- New examples include Google Maps' local pack for nearby coffee shops and a TikTok video for a soccer tutorial, showcasing a more contemporary view of diverse result types
Google November 2023 concludes its core update rollout

Google has officially completed the rollout of its November 2023 core update, marking the fourth broad core algorithm update of the year. It is also the longest-running core update to date.
The update commenced on November 2, 2023, and concluded on November 28, spanning a total of 26 days. This release closely followed the October 2023 core update, which began on October 5 and concluded on October 19. You can find out more about this in our previous blog from October.
The November core update exhibited significant impact and ranking volatility for many websites, with SEOs reporting notable changes early in the rollout. It coincided with the Google November 2023 reviews update, which started on November 8 and is still in progress. Despite the simultaneous rollout, the effects of each update were experienced at different times by various sites.
Understanding and tracking Google algorithm updates is crucial for brands and businesses, as these updates can influence website performance in search results. Positive or negative changes in rankings resulting from a core update can affect organic traffic, conversions, and revenue. Site owners need to be aware of these updates to distinguish between fluctuations caused by site changes and those initiated by Google’s ranking algorithm adjustments.
For websites negatively impacted by a core update, Google has provided advice in the past, emphasizing that there aren’t specific recovery actions to take. A decline in rankings may not necessarily indicate issues with the pages, and recovery, if any, may be observed between core updates, with more substantial changes occurring after subsequent core updates.
Google enhances search with support for organisation metadata

Google has expanded its support for organisation structured data markup, allowing companies to provide more detailed information about themselves in search results. This update enables Google to showcase company details, such as name, address, contact information, and business identifiers, in knowledge panels and other visual elements on the search results page. Previously, Google allowed sites to use “logo” and “url” markup for specifying the image and link for their logo in search results since 2013.
The logo report in Google Search Console and tests in the Rich Results Test tool have transitioned to more comprehensive organisation markup validations. While sites with existing logo markup don’t need to make changes, Google encourages adding the new organisation fields if applicable. This additional information can make companies eligible for expanded knowledge panels, including Google’s recently launched merchant panels.
For local businesses, Google recommends using both local business and organisation markup, while online-only companies should utilise the “OnlineBusiness” subtype of organisation markup. The expansion of organisation structured data aims to make it easier for users to find accurate details in Google Search results. The update highlights the importance of implementing structured data markup, even if not immediately utilised for visible improvements, as it positions sites to benefit from future enhancements when Google’s systems gain the ability to process and display new types of structured data.
Google SGE & generative summaries for search results patent

The recently discovered Google patent, US11769017B1, sheds light on the development of Generative Summaries for Search Results within Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE). This patent outlines a method employing large language models (LLMs) to create concise and contextually rich summaries of search results, revolutionising the search experience.
What is Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE)?
Google’s SGE leverages generative AI to produce snapshots for queries, providing users with immediate insights into topics and facilitating deeper exploration through corroborated links to high-quality web sources. The technology outlined in the patent is integral to SGE, ensuring reliability and breadth in the information provided. We first mentioned this in our blog back in August, where you’ll be able to find out more information on this.
What is the US11769017B1 patent?
The patent introduces a technique for generating search result summaries using LLMs, allowing for a more sophisticated presentation of search results with AI-powered summaries and links for further exploration. It was filed on 20th March, just a few weeks before the announcement of the beta release of SGE.
Below is a summary of how the SGE works according to the patent:
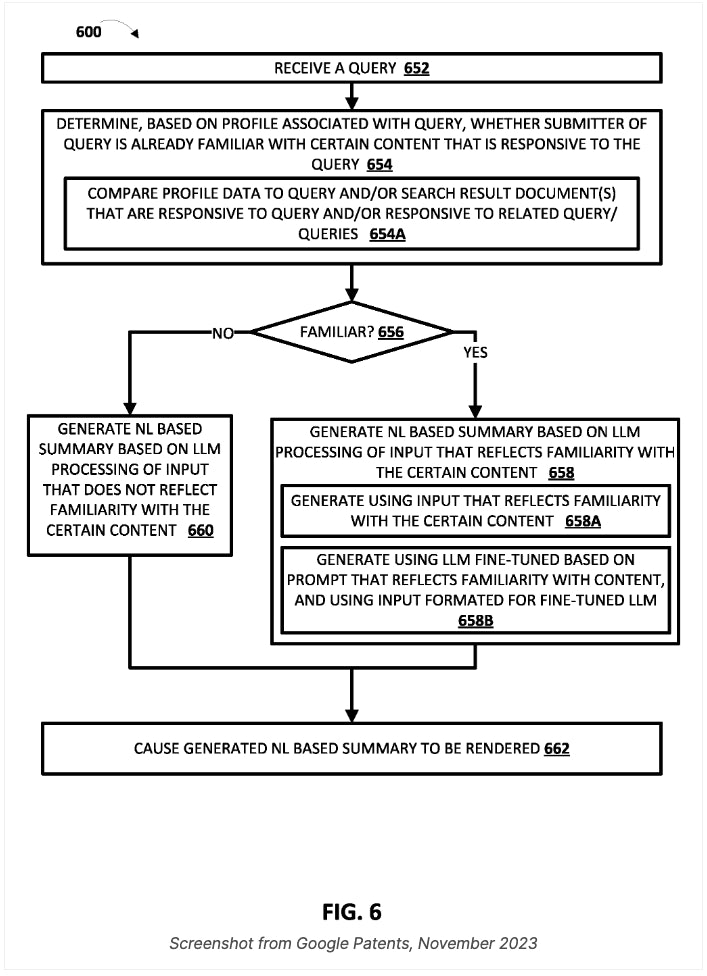
Screenshot taken from Search Engine Journal
What does this mean for SEO professionals and their strategies?
As generative AI becomes integral to search, SEO strategies must adapt to prioritise content aligning with AI-driven summaries. Key takeaways for SEO professionals include:
- Prioritising comprehensive content that thoroughly covers topics and addresses user queries.
- Writing in a clear, concise manner with rich context to increase favorability for summarization by LLMs.
- Optimising content for conversational queries and voice searches.
- Emphasising authority and trustworthiness through citing reputable sources and maintaining factual accuracy.
- Staying updated on trends in generative AI and search to adapt promptly to changes.
SEO professionals are encouraged to stay informed on emerging trends in generative AI and SGE, test the latest updates in Labs, and create diverse content formats. Adapting to changes promptly provides a competitive edge in the evolving landscape of Google search.
In conclusion, Google’s patent and its integration into SGE mark a shift towards more AI-driven, contextually aware search experiences. SEO strategies should align with this evolution by prioritising comprehensive, clear, and authoritative content, optimising for conversational queries, and staying abreast of emerging trends in generative AI and search.
Google rankings prioritise first-hand knowledge

Google recently unveiled a series of search updates aimed at enhancing the user experience. Among these updates are changes in Google’s ranking to make it easier for users to find content that contains personal perspectives or first-hand knowledge. These changes potentially may lead to fewer results that rely on the same second-hand information sources.
In the United States, Google has introduced a feature that allows users to ‘follow’ specific topics through Search. This feature allows users to stay informed with relevant information, significantly enhancing the personalisation of Google.
What does this mean for SEO?
The emphasis on prioritizing firsthand knowledge and unique perspectives underscores the significance of generating content that adds genuine value. With the introduction of the ‘follow’ feature, websites stand to gain increased traffic by producing high-quality content centred around popular topics that users are eager to ‘follow.’ This shift highlights the evolving landscape of SEO, emphasising the importance of relevance and originality in content creation.
Google launches “Notes” to add user comments in search results

In the US and India, Google has launched a new experiment called ‘Notes’ that enables users to view and share tips alongside search results.
By opting in through Google’s Search Labs, users gain the ability to add personalised notes to specific search results and articles directly within the Google app. The driving idea behind ‘Notes’ is to tap into the desire for individuals to gain insights from like-minded people, offering a fresh perspective on search results.
It’s worth noting that Google places a strong emphasis on the safety and quality of content. ‘Notes’ incorporates robust safeguards and human content moderation, mirroring the standards set for conventional Search results.
As this is a new feature, Google has not disclosed how they will provide site owners with insights into notes on their content. However, Google does plan to address this in the future to ensure that site owners understand how this feature may impact them.
Google removing crawl rate limiter tool from Search Console

From 8 January 2024, the search console crawl rate limiter tool will no longer be available. Google has cited improvements in crawling for this.
According to Google, the tool has seen infrequent usage, and when employed, the crawl rate is typically set to the lowest option. Going forward, the default minimum crawl rate will be set to a lower rate that aligns with the preferences commonly requested by publishers.
While the Googlebot report form remains available for reporting unusual Googlebot activities and handling emergency cases, it’s essential to note that the swiftest method for adjusting the crawl rate is through instructing Googlebot via server responses.
Google search algorithm ranking continues

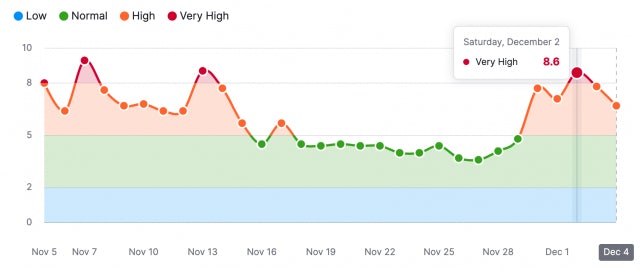
At the beginning of the month, SERoundtable highlighted notable fluctuations and increased discussions regarding Google Search rankings. However, it remains unclear whether these changes were linked to the ongoing November 2023 reviews update, aftershocks from the recently concluded November 2023 core update, or an entirely different cause.
SEOs and website owners saw a significant surge in SEO-related discussions, and many tracking tools continue to display high volatility, surpassing previous levels.
Google’s 2023 search quality rater guidelines update: Here’s what changed

Google continues to redefine its approach to delivering high-quality search results, emphasising the importance of helping Quality Raters understand why certain results offer more value than others. This level of complexity provides insight into the observed fluctuations during Core Updates and beyond.
During core updates, significant shifts in user intent can occur if Google’s quality raters indicate evidence that search results do not align with user expectations. Examining search results before and after major updates becomes more comprehensible when considering the depth of Google’s understanding of query intent and the benchmarks for valuable, high-quality content.
Recent updates in the search quality rater guidelines include:
Enhanced guidance on rating forum and Q&A page quality, particularly for new discussions or those exhibiting “combative,” “misleading,” or “spammy” content
Google emphasises the impact of comments on a page’s overall quality, stressing the significance of well-moderated discussions.

(Found on page 76)
Emphasis on user location’s relevance to certain queries and its influence on search results
The guidelines now highlight the importance of local intent in some search queries compared to more generalised inquiries.

(Found on page 84)
Detailed explanations on “Minor Interpretations,” categorising them into “reasonable,” “unlikely,” and “no chance” interpretations

This classification assists in understanding query meanings that are less expected by users.
Further clarification of ‘Know Simple’ and ‘Do’ queries, outlining specific types of queries that don’t fit the “Know Simple” criteria
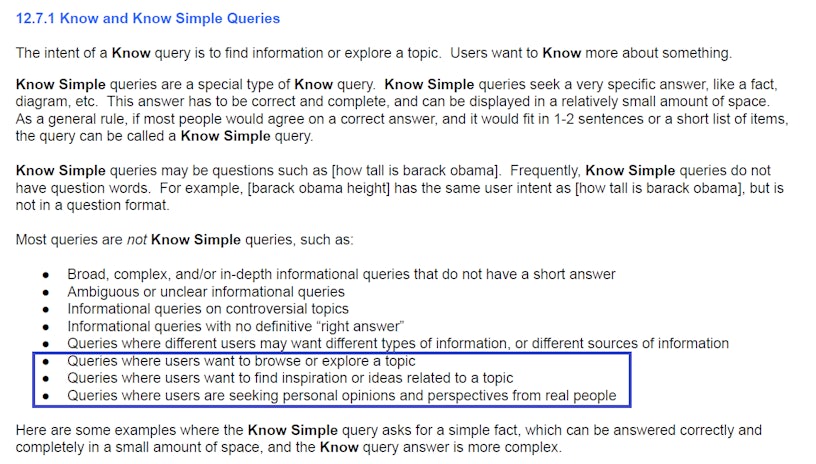
(Found on page 90)
These additions resonate with Google’s Search Generative Experience, potentially aiding in understanding when to initiate such experiences.
Expanded examples of “Know Simple Queries,” “Know Queries,” and “Do” queries, offering insights into queries best answered through videos, images, or how-to guides
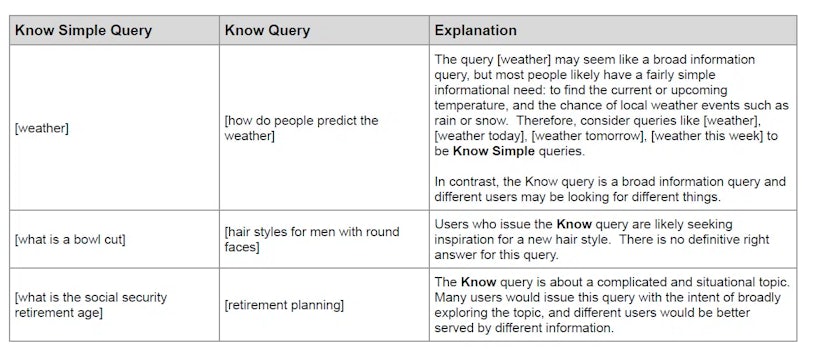
(Found on page 91)
Refinement of user intent language by outlining unlikely intents for certain keywords, helping narrow down user intent to more reasonable expectations.
Examples of SERP features that highly satisfy user needs, with explanations on why these particular results are rated as “highly meeting” user expectations
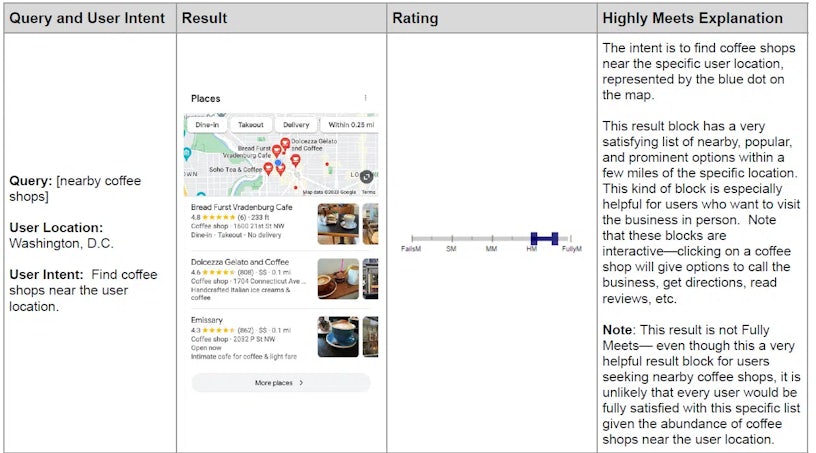
(Found on page 114)
New examples include Google Maps’ local pack for nearby coffee shops and a TikTok video for a soccer tutorial, showcasing a more contemporary view of diverse result types

(Found on page 114)
These updates in the quality rater guidelines reflect Google’s ongoing efforts to provide more nuanced and tailored search experiences that better align with user intents and expectations.
Keep up-to-date with our dedicated algorithm and search industry round-ups. For any further information about these posts – or to learn how we can support your SEO – get in touch today.





